Is the human eye poorly designed? Or is it optimal?
If you ask most proponents of modern evolutionary theory, you will often hear that the eye is a pinnacle of unfortunate evolutionary history and dysteleology.
There are three major arguments that are used in defending this view:
The human eye:
- is inverted (retina) and wired backwards
- has a blind spot due to nerve exit
- Is fragile due to retinal detachment
#1 THE HUMAN EYE IS INVERTED
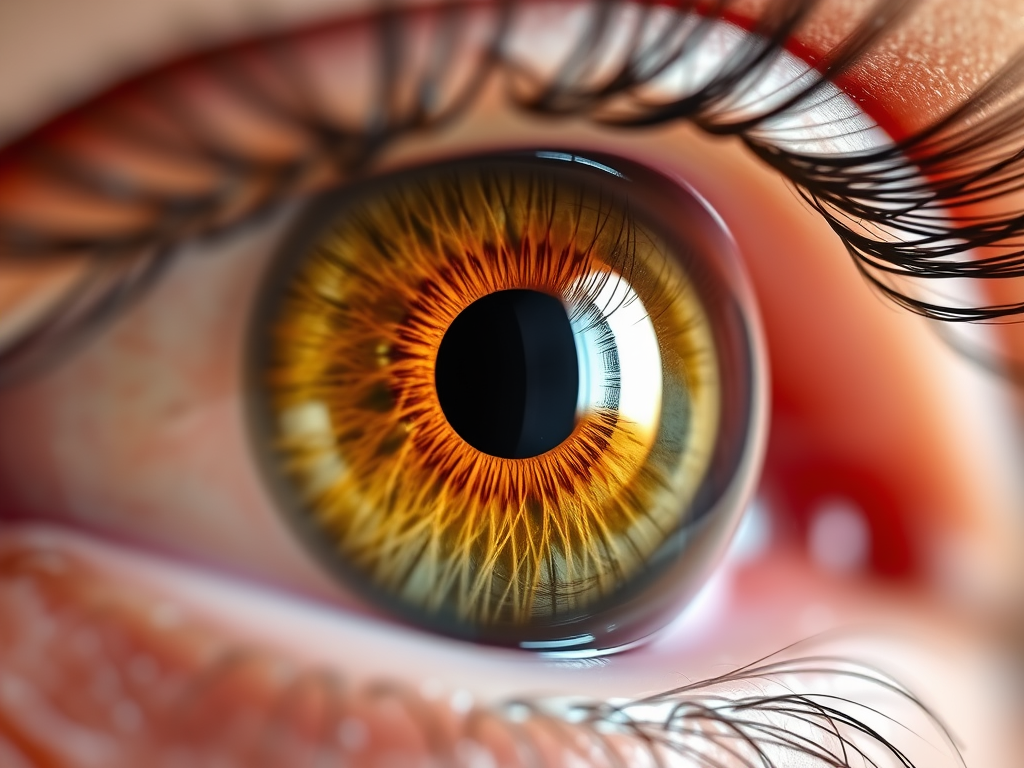
The single most famous critique is, of course, the backward wiring of the retina. An optimal sensor should use its entire surface area for data collection, right? The vertebrate eye requires obstruction of the eye-path by axons and capillaries before it hits the photoreceptors.
Take the cephalopod eye: it has an everted retina, the photo receptors face the light and the nerves are behind them meaning there is no need for a blind spot. The human reversed wiring represents a mere local (rather than global) maximum where the eye could only optimize so far due to its evolutionary history.
Yet, this argument misses non-negotiable constraints. There is a metabolic necessity for the human eye which doesn’t exist in the squid or octopus.
Photoreceptors (the rods and cones) have the highest metabolic rate of any cell in the body. They generate extreme heat and oxygen levels and undergo constant repair from constant reaction from photons. The energy demand is massive. This is an issue of thermoregulation, not just optics.
The reason this is important is because the vertebrate eye is structured with an inverted retina precisely for the survival and longevity of these high-energy photoreceptors. These cells require massive, continuous nutrient and oxygen delivery, and rapid waste removal.
The current inverted orientation is the only geometric configuration that allows the photoreceptors to be placed in direct contact with the Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) and the choroid. The choroid, a vascular layer, serves as the cooling system and high-volume nutrient source, similar to a cooling unit directly attached to a high-performance processor.
If the retina were wired forward, the neural cabling would form a barrier, blocking the connection between the photoreceptors and the choroid. This would inevitably lead to nutrient starvation and thermal damage. Not only that, but human photoreceptors constantly shed toxic outer segments due to damage, which must be removed via phagocytosis by the RPE. The eye needs the tips of the photoreceptors to be physically embedded in the RPE.
If the nerve fibers were placed in front they would form a barrier, preventing waste removal. This specific geometry is a geometric imperative for long-term molecular recycling and allows for eyes that last for 80+ years on the regular.
Critics often insist however that even given the neural and capillary layers being necessary for metabolism, it is still a poor design because they block or scatter incoming light.
Yet, research has demonstrated that Müller glial cells span the thickness of the retina and act as essentially living fiber-optic cables. These cells possess a higher refractive index than the surrounding tissue, which gives them the capability to channel light directly to the cones with minimal scattering.
So this criticism actually goes from being a poor design choice into an awesome low-pass filter which improves the signal-to-noise ratio and visual acuity of the human eye.
But wait, there’s more! The neural layers contain yellow pigments (lutein and zeaxanthin) which absorb excess blue and ultraviolet light that is highly phototoxic! This layer is basically a forcefield against harmful rays (photo-oxidative damage) which extends the lifespan of these super delicate sensors.
#2 THE HUMAN EYE HAS A BLIND SPOT
However, the skeptics will still push back (which leads to point number 2): But surely a good design would not include a blind spot where the optic nerve runs through! And indeed this point is a fairly powerful one at a glance. But on further inspection, we see that this exit point, where literally millions of nerve fibers bundle together to pass the photoreceptors, is an example of optimized routing and not a critical flaw of any kind.
This is true for many reasons. For one, by having the nerves bundle into this reinforced exit point, in this way, maximized the structural robustness of the remaining retina. Basically, if it were not this way, and the nerve fibers exited individually or even in small clusters across the retina, it would radically lower the integrity of the whole design. It would make the retina prone to tearing during rapid eye movements (saccades). In other words, we wouldn’t be getting much REM sleep! That, but also, we’d be missing out on most looking around of any kind.
I’d say, even if that was the only advantage, the loss of a tiny fraction of our visual field is worth the trade-off.
Second, and this is important, the blind spot is functionally irrelevant. What do I mean by that? I mean that humans were designed with two eyes for the purpose of seeing depth-of-field, i.e., understanding where things are in space. You can’t do that with one eye, so that’s not an option. With two eyes, the functional retina of the left eye covers the blind spot of the right eye, and vice versa. There is no problem in this design if both the vision is covered and depth-of-field are covered 100% accurately: which they are.
Third, the optic disc is also used for integrated signal processing, containing melanopsin-driven cells that calibrate brightness perception for the entire eye, using the exit cable as a sensor probe. That means that the nerves also detect brightness and run the logistics in a localized region which is incredibly efficient.
#3 THE HUMAN EYE IS VULNERABLE
That is, the vulnerability specifically refers to retinal detachment. That is when the neural retina separates from the RPE. Why does this happen? It is a consequence of the retina being held loosely against the choroid, largely by hydrostatic pressure. Critics call this a failure point. Wouldn’t a good design be one where the RPE is solidly in place, especially if it needs to be connected to the retina? Well… no, not remotely.
The RPE must actively transport massive amounts of fluid (approximately 10 liters per day) out of the subretinal space to the choroid to prevent edema (swelling) and maintain clear vision. A mechanically fused retina would impede this rapid fluid transport and waste exchange. Basically, the critics offer a solution which is really a non-solution. There is no possible way the eye could function at all by the means they suggest as the alternative “superior” version.
So, what have we learned?
The human eye is not a collection of accidents, but a masterpiece of constrained optimization. When the entire system (eye and brain) is evaluated, the result is astonishing performance. The eye achieves resolution at the diffraction limit (the theoretical physical limit imposed by the wave nature of light!) at the fovea, meaning it is hitting the maximum acuity possible for an aperture of its size.
The arguments that the eye is “sub-optimal” often rely on comparing it to the structurally simpler cephalopod eye. Yet, cephalopod eyes lack trichromatic vision (they don’t see color like we do), have lower acuity (on the scale of hundreds of times worse clarity), and only function for a lifespan of 1–2 years (whereas the human eye must self-repair and maintain high performance for eight decades). The eye’s complexity—the Müller cells, the foveal pit, and the inverted architecture—are the necessary subsystems required to achieve this maximal performance within the constraints of vertebrate biology and physics.
That’s not even getting to things like mitochondrial microlens in our cells which are essential for processing light. Recent research suggests that mitochondria in cone photoreceptors may actually function as micro-lenses to concentrate light, adding another layer of optical optimization. Optimization which would need to be there, perhaps a lot earlier than even the reversed lens structure.
The fact that the eye is so optimal still remains, despite the critics best attempts at thwarting it. Therefore, the question remains, how could something so optimized evolve by random chance mutation, as well as so early and often in the history of biota?




Leave a comment